Medicare Refers to the Medical Insurance Program Established to Help Low Income Families. True False
By The Democracy Fund
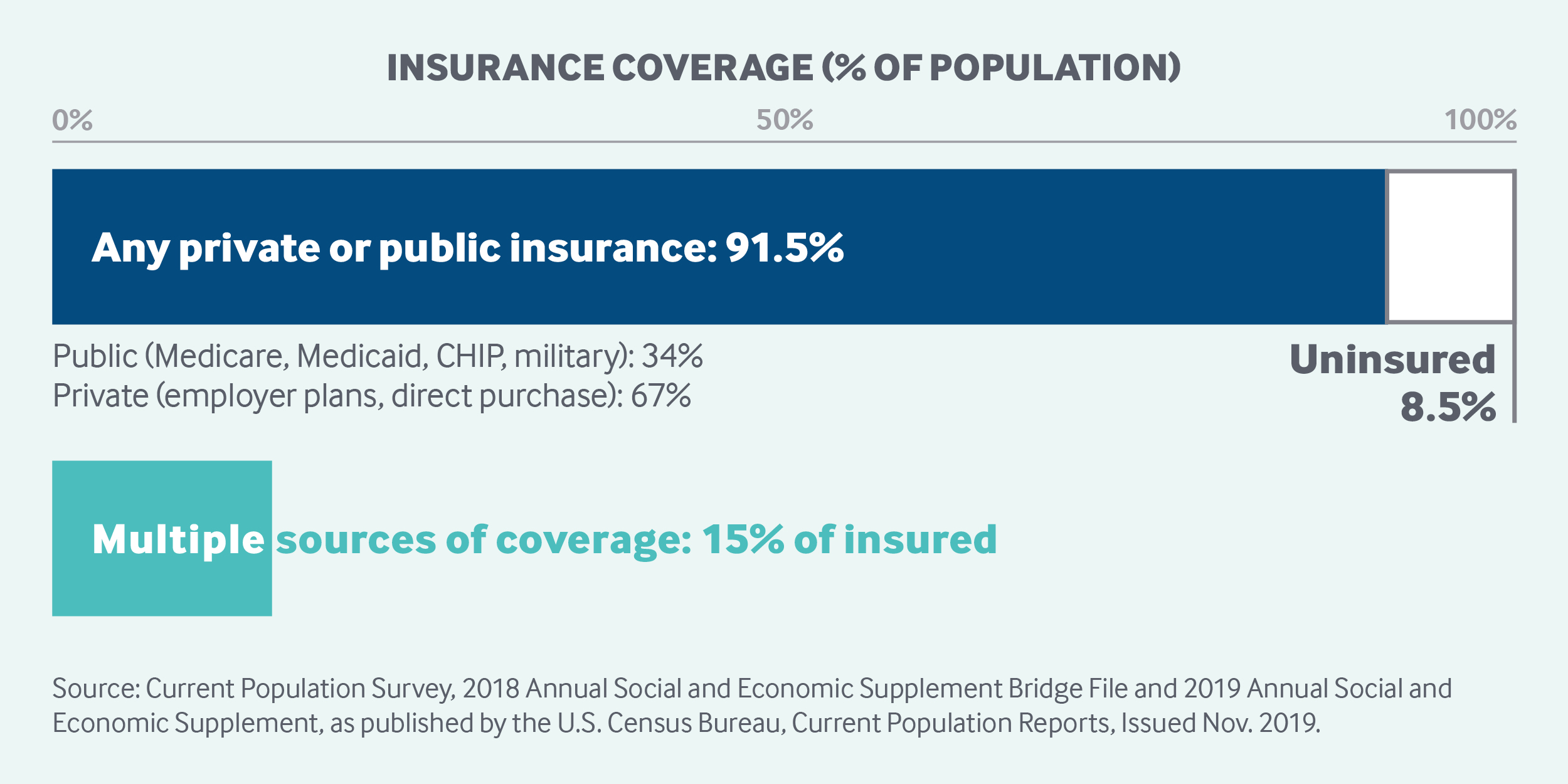
The U.Southward. health system is a mix of public and private, for-profit and nonprofit insurers and wellness care providers. The federal regime provides funding for the national Medicare program for adults historic period 65 and older and some people with disabilities besides as for various programs for veterans and low-income people, including Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Plan. States manage and pay for aspects of local coverage and the safety internet. Private insurance, the ascendant form of coverage, is provided primarily by employers. The uninsured rate, 8.five percent of the population, is down from 16 percent in 2010, the year that the landmark Affordable Care Human action became law. Public and private insurers set their own benefit packages and cost-sharing structures, within federal and state regulations.
How does universal health coverage work?
The United states of america does not have universal wellness insurance coverage. Nearly 92 pct of the population was estimated to have coverage in 2018, leaving 27.5 million people, or 8.five percent of the population, uninsured.1 Movement toward securing the right to health care has been incremental.two
Employer-sponsored health insurance was introduced during the 1920s. It gained popularity afterward World War II when the authorities imposed wage controls and declared fringe benefits, such as wellness insurance, taxation-exempt. In 2018, most 55 per centum of the population was covered under employer-sponsored insurance.three
In 1965, the beginning public insurance programs, Medicare and Medicaid, were enacted through the Social Security Act, and others followed.
Medicare. Medicare ensures a universal right to health care for persons historic period 65 and older. Eligible populations and the range of benefits covered accept gradually expanded. In 1972, individuals under age 65 with long-term disabilities or end-phase renal affliction became eligible.
All beneficiaries are entitled to traditional Medicare, a fee-for-service program that provides infirmary insurance (Office A) and medical insurance (Role B). Since 1973, beneficiaries have had the option to receive their coverage through either traditional Medicare or Medicare Reward (Office C), under which people enroll in a private health maintenance organization (HMO) or managed intendance arrangement.
In 2003, Part D, a voluntary outpatient prescription drug coverage choice provided through individual carriers, was added to Medicare coverage.
Medicaid. The Medicaid program beginning gave states the option to receive federal matching funding for providing health care services to low-income families, the bullheaded, and individuals with disabilities. Coverage was gradually made mandatory for low-income pregnant women and infants, and subsequently for children upwardly to age 18.
Today, Medicaid covers 17.9 pct of Americans. As it is a state-administered, means-tested program, eligibility criteria vary by land. Individuals demand to apply for Medicaid coverage and to re-enroll and recertify annually. As of 2019, more than 2-thirds of Medicaid beneficiaries were enrolled in managed intendance organizations.iv
Children's Health Insurance Program. In 1997, the Children'south Wellness Insurance Program, or CHIP, was created as a public, land-administered plan for children in low-income families that earn as well much to qualify for Medicaid but that are unlikely to exist able to afford private insurance. Today, the plan covers 9.6 1000000 children.5 In some states, it operates equally an extension of Medicaid; in other states, it is a dissever programme.
Affordable Care Act. In 2010, the passage of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Human activity, or ACA, represented the largest expansion to date of the government'south part in financing and regulating health intendance. Components of the law'due south major coverage expansions, implemented in 2014, included:
-
requiring most Americans to obtain health insurance or pay a penalty (the penalty was later removed)
-
extending coverage for young people by assuasive them to remain on their parents' private plans until age 26
-
opening health insurance marketplaces, or exchanges, which offer premium subsidies to lower- and middle-income individuals
-
expanding Medicaid eligibility with the help of federal subsidies (in states that chose this pick).
The ACA resulted in an estimated 20 million gaining coverage, reducing the share of uninsured adults anile 19 to 64 from twenty percent in 2010 to 12 percent in 2018.half dozen
Role of regime: The federal government'due south responsibilities include:
-
setting legislation and national strategies
-
administering and paying for the Medicare programme
-
cofunding and setting basic requirements and regulations for the Medicaid plan
-
cofunding CHIP
-
funding health insurance for federal employees equally well as active and by members of the military and their families
-
regulating pharmaceutical products and medical devices
-
running federal marketplaces for private health insurance
-
providing premium subsidies for private marketplace coverage.
The federal regime has just a negligible function in straight owning and supplying providers, except for the Veterans Health Administration and Indian Wellness Service. The ACA established "shared responsibility" among government, employers, and individuals for ensuring that all Americans have access to affordable and good-quality health insurance. The U.S. Section of Health and Human being Services is the federal regime'southward principal agency involved with health care services.
The states cofund and administer their CHIP and Medicaid programs according to federal regulations. States set up eligibility thresholds, patient cost-sharing requirements, and much of the benefit package. They also assistance finance health insurance for land employees, regulate private insurance, and license health professionals. Some states also manage wellness insurance for low-income residents, in addition to Medicaid.
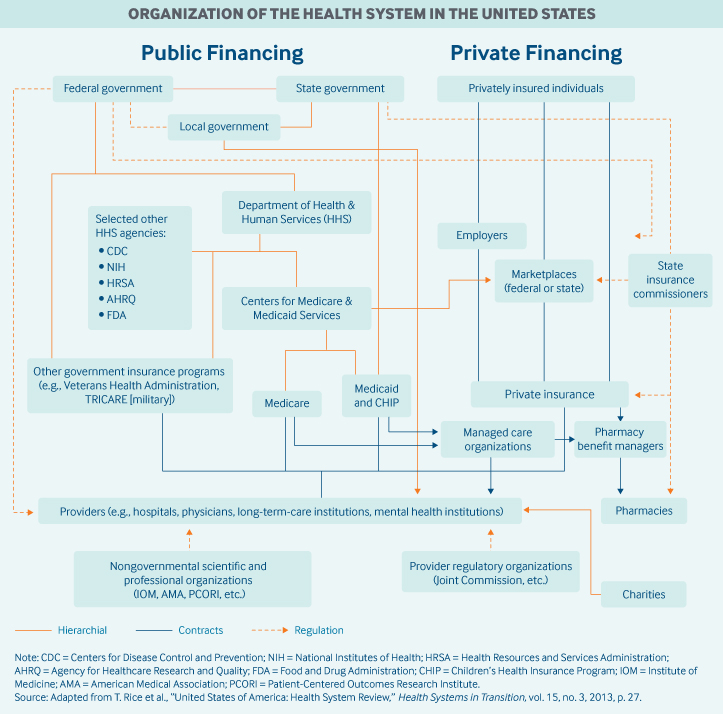
Role of public health insurance: In 2017, public spending deemed for 45 percent of total wellness care spending, or approximately eight percentage of Gdp. Federal spending represented 28 percent of total wellness care spending. Federal taxes fund public insurance programs, such as Medicare, Medicaid, CHIP, and military health insurance programs (Veteran's Health Administration, TRICARE). The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services is the largest governmental source of health coverage funding.
Medicare is financed through a combination of general federal taxes, a mandatory payroll tax that pays for Part A (infirmary insurance), and individual premiums.
Medicaid is largely revenue enhancement-funded, with federal tax revenues representing two-thirds (63%) of costs, and land and local revenues the rest.7 The expansion of Medicaid under the ACA was fully funded by the federal government until 2017, after which the federal funding share gradually decreased to xc percent.
CHIP is funded through matching grants provided past the federal government to states. Well-nigh states (30 in 2018) charge premiums nether that plan.
Role of private health insurance: Spending on private wellness insurance accounted for ane-3rd (34%) of full health expenditures in 2018. Private insurance is the primary health coverage for two-thirds of Americans (67%). The bulk of private insurance (55%) is employer-sponsored, and a smaller share (xi%) is purchased past individuals from for-turn a profit and nonprofit carriers.
About employers contract with individual health plans to administer benefits. Most employer plans cover workers and their dependents, and the majority offer a choice of several plans.8,nine Both employers and employees typically contribute to premiums; much less frequently, premiums are fully covered by the employer.
The ACA introduced a federal marketplace, HealthCare.gov, for purchasing individual primary health insurance or dental coverage through individual plans. States can besides prepare their ain marketplaces.
More than ane in iii Medicare beneficiaries in 2019 opted to receive their coverage through a private Medicare Advantage health plan.10
Medicaid beneficiaries may receive their benefits through a private managed care organization, which receives capitated, typically risk-adjusted payments from land Medicaid departments. More than ii-thirds of Medicaid beneficiaries are enrolled in managed care.
Services covered: There is no nationally divers benefit packet; covered services depend on insurance blazon:
Medicare. People enrolled in Medicare are entitled to infirmary inpatient care (Part A), which includes hospice and curt-term skilled nursing facility care.
Medicare Part B covers physician services, durable medical equipment, and home health services. Medicare covers short-term post-acute care, such as rehabilitation services in skilled nursing facilities or in the home, but not long-term care.
Part B covers but very limited outpatient prescription drug benefits, including injectables or infused drugs that need to exist administered by a medical professional in an role setting. Individuals can buy private prescription drug coverage (Office D).
Coverage for dental and vision services is limited, with virtually beneficiaries lacking dental coverage.11
Medicaid. Under federal guidelines, Medicaid covers a wide range of services, including inpatient and outpatient hospital services, long-term care, laboratory and diagnostic services, family planning, nurse midwives, freestanding nascency centers, and transportation to medical appointments.
States may cull to offer additional benefits, including physical therapy, dental, and vision services. Most states (39, equally of 2018) provide dental coverage.12
Outpatient prescription drugs are an optional benefit under federal law; however, currently all states provide drug coverage.
Private insurance. Benefits in private health plans vary. Employer wellness coverage usually does not cover dental or vision benefits.13
The ACA requires individual marketplace and small-group market plans (for firms with 50 or fewer employees) to cover x categories of "essential health benefits":
-
convalescent patient services (doctor visits)
-
emergency services
-
hospitalization
-
maternity and newborn intendance
-
mental health services and substance employ disorder handling
-
prescription drugs
-
rehabilitative services and devices
-
laboratory services
-
preventive and health services and chronic disease management
-
pediatric services, including dental and vision care.
Cost-sharing and out-of-pocket spending: In 2018, households financed roughly the aforementioned share of total health care costs (28%) as the federal government. Out-of-pocket spending represented approximately one-third of this, or 10 percent of total wellness expenditures. Patients usually pay the full cost of care up to a deductible; the average for a unmarried person in 2018 was $1,846. Some plans encompass primary care visits before the deductible is met and crave but a copayment.
Out-of-pocket spending is considerable for dental care (40% of full spending) and prescribed medicines (14% of total spending).14
Condom nets: In improver to public insurance programs, including Medicare and Medicaid, taxpayer dollars fund several programs for uninsured, low-income, and vulnerable patients. For instance, the ACA increased funding to federally qualified health centers, which provide primary and preventive care to more than 27 1000000 underserved patients, regardless of ability to pay. These centers charge fees based on patients' income and provide free vaccines to uninsured and underinsured children.15
To assistance offset uncompensated intendance costs, Medicare and Medicaid provide asymmetric-share payments to hospitals whose patients are mostly publicly insured or uninsured. State and local taxes assistance pay for boosted clemency care and condom-net programs provided through public hospitals and local wellness departments.
In addition, uninsured individuals accept access to acute intendance through a federal law that requires most hospitals to care for all patients requiring emergency care, including women in labor, regardless of ability to pay, insurance condition, national origin, or race. Every bit a consequence, private providers are a significant source of clemency and uncompensated care.
How is the delivery system organized and how are providers paid?
Doc instruction and workforce: Most medical schools (59%) are public. Median tuition fees in 2019 were $39,153 in public medical schools and $62,529 in private schools. Near students (73%) graduate with medical debt averaging $200,000 (2019), an amount that includes pre-medical education.21 Several federal debt-reduction, loan-forgiveness, and scholarship programs are offered; many target trainees for placement in underserved regions. Providers practicing in designated Health Professional Shortage Areas are eligible for a Medicare physician bonus payment.
Master care: Roughly one-third of all professionally agile doctors are chief care physicians, a category that encompasses specialists in family medicine, full general exercise, internal medicine, pediatrics, and, according to some, geriatrics. Approximately one-half of chief care doctors were in physician-endemic practices in 2018; more usually, these are general internists rather than family unit practitioners.22
Chief intendance physicians are paid through a combination of methods, including negotiated fees (private insurance), capitation (individual insurance and some public insurance), and administratively fix fees (public insurance). The majority (66%) of primary care practice revenues come from fee-for-service payments.23 Since 2012, Medicare has been experimenting with alternative payment models for principal care and specialist providers.
Outpatient specialist intendance: Specialists can work both in private practices and in hospitals. Specialist practices are increasingly integrating with hospital systems, likewise equally consolidating with each other. The majority of specialists are in grouping practices, most often in single-specialty group practices.24
Outpatient specialists are free to choose which form of insurance they volition accept. For example, not all specialists accept publicly insured patients, considering of the relatively lower reimbursement rates set by Medicaid and Medicare. Access to specialists for beneficiaries of these programs—not to mention for people without whatsoever insurance—tin can therefore be particularly limited.
Authoritative mechanisms for direct patient payments to providers: Copayments for doctor visits are typically paid at the time of service or billed to the patient afterward. Some insurance plans and products (including wellness savings accounts) require patients to submit claims to receive reimbursement.
Providers bill insurers past coding the services rendered. There are thousands of codes, making this process time-consuming; providers typically rent coding and billing staff.
Because of administrative hurdles, a small number of providers do non have any insurance. Instead, they accept only cash payments or require almanac or monthly retainer payments to the providers for "concierge medicine," which offers enhanced access to services.
After-hours care: Primary care physicians are not required to provide or plan for after-hours access for their registered patients. Withal, in 2019, 45 percent of primary intendance doctors had after-hours arrangements: 38 per centum of these provide care in the evenings and 41 percent on the weekends.25
After-hours intendance is increasingly provided through walk-in appointments at private urgent-intendance centers or retail clinics that typically serve younger, healthier individuals who require episodic intendance and may not have a primary care provider.26
Hospitals: In 2018, 57 percent of the 5,198 brusk-term acute intendance hospitals in the U.S. were nonprofit; 25 percent were for-turn a profit; and 19 percent were public (state or local government–endemic).27 In addition, there were 209 federal government hospitals.
Hospitals are complimentary to choose which insurance they have; most take Medicare and Medicaid. Hospitals are paid through a combination of methods.
-
Medicare pays hospitals through prospective diagnosis-related group (DRG) rates, which do not include doctor payments.
-
Medicaid pays hospitals on a DRG, per diem, or cost-reimbursement basis,28 and states have considerable discretion in setting infirmary payment rates.
-
Private insurers pay hospitals ordinarily on a per diem ground, typically negotiated betwixt each infirmary and its insurers on an annual ground.
Mental wellness care: Services are provided past both generalists and specialists—including primary care physicians, psychiatrists, psychologists, social workers, and nurses—with the majority delivered in an outpatient setting. Providers are mostly private (nonprofit and for-profit), with some public providers, including public mental health hospitals, Veterans Diplomacy providers, and federally qualified health centers.
The federal Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration provides states with grants, including Mental Wellness Block Grants, that fund community mental health services. State and local governments provide additional funding.
The ACA mandated that marketplace insurers provide coverage of mental wellness and substance utilize weather condition as an essential health benefit. The law besides requires all private insurers, including employer-sponsored plans, to provide the aforementioned level of benefits for mental and physical wellness atmospheric condition.
Some individuals with serious, long-term mental illnesses qualify for Medicare earlier age 65. Otherwise, Medicaid is the single largest source of funding for mental health services in the country.29 Many employer-sponsored plans and some state Medicaid programs provide benefits through carve-out contracts with managed behavioral health care organizations.30
Long-term care and social supports: In that location is no universal coverage for long-term care services. Public spending represents approximately 70 per centum of total spending on long-term care services, with Medicaid accounting for the majority.31 Medicare and nearly employer-sponsored plans cover merely mail–astute care services following hospitalization, including hospice, short-term nursing services, and short-term nursing home stays (up to 100 days following acute hospitalization).
Individual long-term care insurance is bachelor merely rarely purchased; private insurance represented simply seven.5 per centum of total long-term intendance spending in 2016.
The ACA originally included the Community Living Assistance Services and Supports Human activity, which would have created a universal, voluntary, public long-term care insurance choice for employed persons. However, the program was accounted unworkable and was repealed in 2013.
What are the major strategies to ensure quality of intendance?
The ACA required the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to constitute a National Quality Strategy,32 a set of national aims and priorities to guide local, state, and national quality comeback efforts, supported by partnerships with public and private stakeholders. The strategy includes annual reporting on a selected set of quality measures.33
Since 2003, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality has published the annual National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report, which reports on national progress in health care quality improvement. The 2018 study plant that the quality of U.S. health intendance had improved overall from 2000 to 2016, but that comeback was inconsistent. For example, while about person-centered care and patient-prophylactic measures improved, affordability did not.34
Federal law requires certain providers to report data on the quality of their intendance, and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to publicly study performance on quality measures. For instance, Hospital Compare is an online public resource summarizing the performance of more than 4,000 hospitals on measures of intendance processes, care outcomes, and patient experiences. Related quality-reporting programs include Nursing Domicile Compare and Physician Compare.
The Healthcare Effectiveness Information and Data Gear up is one of the nigh widely used tools for rating provider quality. It is used by wellness plans to rate provider quality. The set includes rates of cancer screenings, medication direction for chronic weather condition, follow-up visits, and other metrics. The nonprofit National Quality Forum builds consensus on national functioning measurement and priorities, including the submission of recommendations for measures to be used in Medicare.
What is beingness done to reduce disparities?
Several federal agencies are tasked with monitoring and reducing disparities. The Bureau for Healthcare Research and Quality publishes an almanac national report highlighting disparities in health care quality by race/ethnicity, age, and sex. Co-ordinate to the latest study, disparities related to income and race persist simply grew smaller between 2000 and 2016.35 African Americans, American Indians, Alaska Natives, Native Hawaiians, and Pacific Islanders received worse intendance than whites according to about 40 percentage of quality measures. Hispanics and Asian Americans received worse care per 35 per centum and 28 pct of measures, respectively. Disparities for poor and uninsured populations are too persisting in major priority areas for quality.
Certain federal offices have specific responsibilities related to reducing disparities:
-
The Part of Minority Health is tasked with developing policies and programs to eliminate disparities among racial and ethnic minority groups.
-
The Health Resource and Services Administration is tasked with providing grants to states, local governments, and customs-based organizations for care and treatments for low-income, uninsured, or other vulnerable populations, including specific programs targeting individuals with HIV/AIDS, mothers and children (through the Maternal and Child Health Bureau), and rural or remote populations.36 The agency also houses the Office of Health Equity, which works to reduce wellness disparities.
-
The Indian Health Service serves two.6 million American Indians and Alaska Natives who belong to more than than 500 federally recognized tribes in 37 states. The service is fully funded through the federal authorities.
The ACA created a legal requirement for nonprofit hospitals, which are exempt from paying sure taxes because of their charitable status, to deport community health needs assessments together with community stakeholders to identify and accost unmet wellness needs in their communities. This requirement is enforced through the Internal Revenue Service, and reporting must be fabricated bachelor to the public.37
What is being done to promote commitment arrangement integration and intendance coordination?
The ACA introduced several levers to improve the coordination of care amongst medical/clinical providers in the largely specialist-driven wellness intendance organisation. For case, the law supported adoption of the "patient-centered medical home" model, which emphasizes care continuity and coordination via primary care, as well equally show-based care, expanded access, and prevention and chronic care direction.
The ACA as well expanded the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services' ability to exam alternative payment models that advantage quality, reduce costs, and aim to improve care coordination. This trend has since been continued by public and private payers.
One of these culling payment models is "bundled payments," whereby a single payment is made for all the services delivered by multiple providers for a single episode of intendance. Another trend is the proliferation of accountable care organizations (ACOs). These networks of providers presume contractual responsibility for providing a defined population with care that meets quality targets. Providers in ACOs share in the savings that constitute the deviation between forecasted and actual wellness care spending.
As of 2019, there were more than ane,000 ACOs in the public and private markets, covering 32.vii one thousand thousand people. Of these ACOs, 558 are Medicare ACOs, serving 12.3 million beneficiaries who are gratis to seek services from any Medicare provider, including those exterior their designated ACO.38,39,40 There are many variants of the Medicare ACO: The most pop is a permanent programme written into the ACA, the Medicare Shared Savings Program, which serves nearly one-third of all Medicare beneficiaries. To improve coordination, ACOs are implementing programs that include medication direction, prevention of emergency department visits and hospital readmissions, and management of high-demand, high-cost patients.
What is the condition of electronic health records?
The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Data Technology, created in 2004, is the principal federal entity charged with the coordination of nationwide efforts to implement and advance the use of wellness information technology and the electronic exchange of health infor-mation. In 2017, an estimated 96 percent of nonfederal astute care hospitals and 86 percent of office-based physicians had adopted a "certified" electronic wellness record (EHR) arrangement. Eighty percent of hospitals and 54 percentage of physician offices had adopted an EHR with avant-garde ca-pabilities, such every bit the ability to track patient demographics, list medications, store clinician notes, and track medication orders, laboratory tests, and imaging results.41,42
The 21st Century Cures Act, passed in 2016 to promote the use of EHRs overall, requires that all wellness care providers brand electronic copies of patient records available to patients, at their request, in machine-readable grade.
How are costs contained?
Annual per capita wellness expenditures in the United States are the highest in the globe (USD $11,172, on average, in 2018), with health care costs growing between 4.2 percent and five.eight percent annually over the past five years.43
Private insurers accept introduced several demand-side levers to control costs, including tiered provider pricing and increased patient price-sharing (for example, through the contempo proliferation of high-deductible wellness plans). Other levers include price negotiations, selective provider contracting, risk-sharing payments, and utilization controls.
The federal government controls costs by:
-
setting provider rates for Medicare and the Veterans Health Administration
-
capitating payments to Medicaid and Medicare managed care organizations
-
capping almanac out-of-pocket fees for beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans and individuals enrolled in marketplace/exchange plans
-
negotiating drug prices for the Veterans Health Administration.
Notwithstanding, since near Americans accept private health insurance, there are limited options bachelor to the federal authorities. The ACA introduced cost-control levers for private insurers offer marketplace coverage, requiring that insurers planning to significantly increment plan premiums submit their prospective rates to either the land or the federal government for review.
State governments try to control costs by regulating individual insurance, setting Medicaid provider fees, developing preferred-drug lists, and negotiating lower drug prices for Medicaid. Maryland and Massachusetts estimate total statewide health expenditures and set annual growth benchmarks for wellness care costs across payers. In those states, health care entities are required to implement performance improvement plans if they do not run across the benchmark.
Attempts to contain pharmaceutical spending are limited to a few mechanisms:
-
The prices private health plans pay for prescription drugs are based on formularies.
-
Pharmacy benefit managers are tasked with negotiating drug prices and rebates with manufacturers on behalf of individual insurers.
-
Volume-based rebates are commonly used past payers and manufacturers to offset the prices of drugs with therapeutic substitutes.
-
Prior authorizations and footstep therapy encourage the use of lower-cost alternatives.
Amid public payers, the Veterans Wellness Assistants receives the deepest discounts for medicines. The bureau is legally entitled to a minimum 24 per centum discount from the nonfederal average manufacturer price and tin cull to negotiate deeper discounts with manufacturers. Medicaid besides is legally entitled to a discounted cost and tin negotiate further discounts.44 Medicare, the largest buyer of prescription drugs, does not negotiate drug costs with manufacturers.
What major innovations and reforms have recently been introduced?
Medicare and Medicaid Innovations. The Affordable Care Act ushered in sweeping insurance and health organisation reforms aimed at expanding coverage, addressing affordability, improving quality and efficiency, lowering costs, and strengthening primary and preventive care and public health. The most important engine for innovation is the new Heart for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation. The ACA allocated $10 billion over x years to the bureau with the mandate to bear research and development that tin improve the quality of Medicare and Medicaid services, reduce their costs, or both.
If initiatives undertaken past the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation are certified by federal actuaries every bit improving quality of care at the same price—or maintaining quality while reducing health care costs—the U.South. Secretary of Health and Human being Services has the authority to spread these initiatives, without congressional blessing, throughout the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
The Trump administration has rolled out several other changes to the Medicare and Medicaid programs. These include the 2019 annunciation of Primary Intendance First, a new voluntary payment model intended for launch in 2021 that aims to simplify principal care physician payments. In addition, since 2018, several states have instated a requirement for able-bodied individuals to document that they are coming together minimum work requirements to authorize for or go on their Medicaid coverage.
Changes to the Affordable Care Act. Every bit of 2020, most of the ACA's provisions remain the law of the land. However the Trump administration has canceled some consumer protections through regulatory and executive actions. For instance, in 2019, the individual mandate, the financial penalty for non having health insurance, was removed. In addition, through executive orders enacted in 2017 and 2018, the administration allowed states to offering alternative, lower-cost, minimally regulated insurance plans in their marketplaces that do not run across the minimum requirements of the ACA.
Cost Command Initiatives. The assistants has also appear efforts to address high health intendance prices, especially concerning prescription drugs. Two bills passed in 2018 banned so-called "gag clauses" in contracts betwixt pharmacies and pharmacy do good managers. These clauses prevented pharmacists from informing customers when the cash price (without billing insurance) for a drug is lower than the insurance-negotiated toll. In addition, to address hospital price transparency, federal rules require all hospitals to post their charges for medical procedures online and update the list at least one time a yr.
The by few years take likewise seen employers, which provide health insurance for approximately half of Americans, taking strides to lower wellness intendance costs by eliminating "middleman" agents—such equally insurance companies and pharmaceutical benefit managers—from the health care financing chain. Some larger employers take joined with others to form their ain nonprofit health intendance corporations, with the articulation venture between Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and J.P. Morgan being one prominent example.45 Other firms, such as Apple tree, are hiring providers directly to evangelize care to their employees at on-site health clinics.46
Source: https://www.commonwealthfund.org/international-health-policy-center/countries/united-states
0 Response to "Medicare Refers to the Medical Insurance Program Established to Help Low Income Families. True False"
Post a Comment